News
E-Ring – Shaft E-Ring
E-Ring (E-Type Shaft Retaining Ring)
The E-Ring, also known as the E-Type Shaft Retaining Ring or E-Clip, is a common mechanical component primarily used to secure bearings, gears, or other parts, preventing them from sliding or falling off the shaft. It has an incomplete circular shape, with several protruding teeth on the inner side that help it snap into the groove on the shaft.
Specifications of E-Rings
The main specifications of E-Rings include:
Inner Diameter: The diameter of the inner circle of the E-Ring, which must match the shaft diameter.
Thickness: The thickness of the E-Ring, affecting its strength and load-bearing capacity.
Material: As mentioned, E-Rings come in a variety of materials.
C-Ring – Shaft C-Ring
C-Type Retaining Ring
The C-Type Retaining Ring is a common mechanical component widely used in various mechanical devices. It is named for its shape, which resembles the letter "C". Typically made from metal materials such as stainless steel or carbon steel, it features elasticity that allows it to securely fasten parts and prevent them from loosening.
Generally, it is a circular hardware fastener with a C-shaped opening, designed for connecting and securing components either temporarily or permanently. C-type retaining rings are widely used across many industries, including machinery, construction, electronics, and automotive sectors.
Spiral Springs – Springs
A spiral spring, also known as a mainspring, is a type of spring made by winding a strip of material into a spiral shape.
As a specialized type of spring, the spiral spring offers unique advantages and has a wide range of potential applications. When selecting a spiral spring, it is important to consider multiple factors to ensure that the chosen spring meets the actual requirements.
Spring Selection
The types of springs are diverse, ranging from common helical springs to complex bent springs. Each type of spring has its unique characteristics and applications. When choosing the appropriate spring, the following factors should be considered:
Material Selection: Spring materials include SUS304, SUS316, SUS631, SWP, SWC, spring steel, phosphor bronze wire, beryllium copper wire, and others.
Spring Types: Compression springs, tension springs, torsion springs, spiral springs, bent components, wire-formed springs, retaining rings, special-shaped springs, leaf springs, etc.
Spring Function: This should be determined based on the customer’s needs. Compression springs focus on compressive force during the compression stroke, tension springs are designed for the tensile load in the extension stroke, and torsion springs provide torsional force during angular displacement.
Working Environment: Extreme temperatures can affect the elasticity of springs. High humidity may cause corrosion of the spring. Corrosive environments, such as acidic or alkaline conditions, can accelerate spring corrosion.
Load Conditions:
Static Load: Stable load, mainly considering the spring’s stiffness.
Dynamic Load: Rapidly changing load, requiring consideration of the spring’s fatigue life.
Impact Load: Instantaneous high load, requiring consideration of the spring’s toughness.
Space Limitations:
Installation Space: The spring's size and shape must fit the installation space.
Interference: The spring's movement range must not interfere with other components.
How to Choose the Right Spring:
Consult Ruisheng Hardware Spring Manufacturers, where professional staff will design and advise you, and evaluate any issues related to load, dimensions, and compatibility.
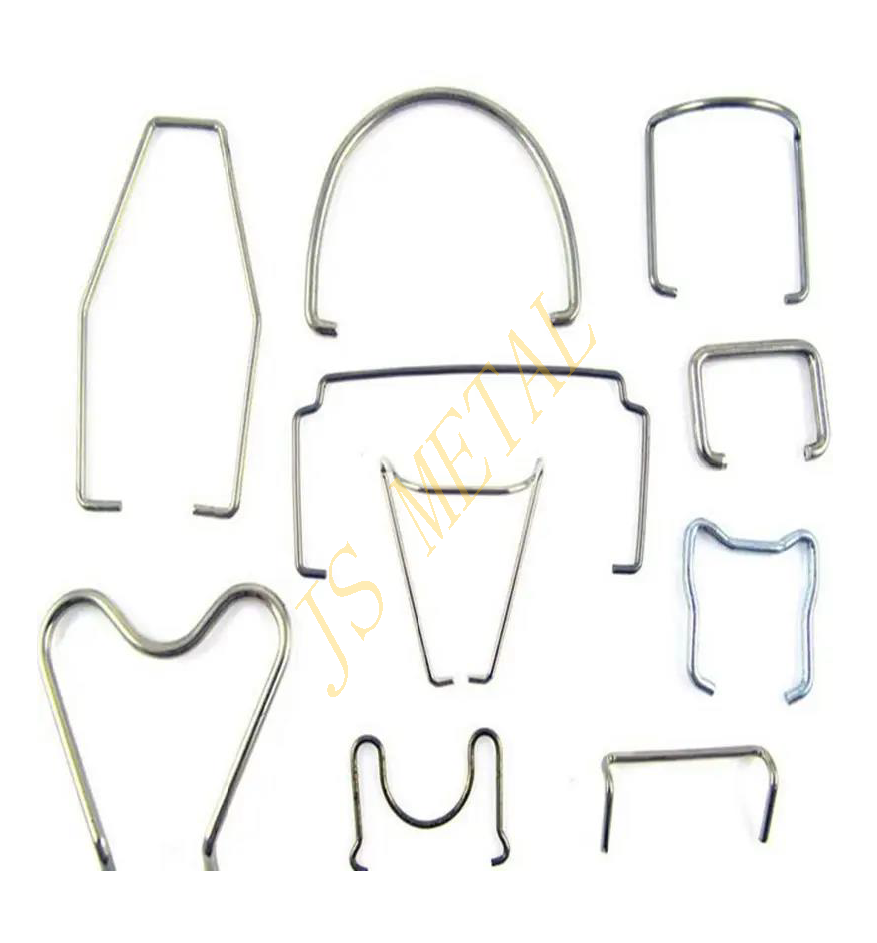
Wire-formed Spring/Bent Component Spring
Wire-formed Springs, also known as Bent Component Springs, are made by bending and shaping spring wire into various forms and non-standard, specialized spring shapes. These are typically customized according to the client's specific design and application needs. The shape of bent component springs is more diverse, offering higher design flexibility, and can meet a wide range of complex application requirements.
Tension spring-Springs
A tension spring is a common mechanical component, and its elastic properties make it widely used in many fields. When selecting a tension spring, it is necessary to consider factors such as material, size, and spring force, based on the specific application requirements.。
Torsion Spring-What is a double torsion spring?
A torsion spring is a type of spring that works by twisting to store mechanical energy in the form of rotational force. A double torsion spring, also known as a dual torsion spring, consists of two torsion springs connected together, usually in a way that allows for opposing forces. This configuration helps balance the applied forces, providing torque in both directions. Double torsion springs are commonly used in applications where equal torque is required in opposite directions, such as in mechanical devices like clothespins, mousetraps, or other mechanisms that need equal tension on both sides.
Tension Spring-English hook
The "English hook tension spring" is the most common type of tension spring, characterized by special hook-shaped designs at both ends. These hooks are typically bent at a 90-degree angle, making it easy to connect to other components. When a tensile force is applied, the spring elongates, storing energy, and returns to its original shape after the force is released.
Both ends have 90-degree bent hooks, making them easy to connect.
It can elongate under tensile force and return to its original shape when the force is released.
Widely used in various mechanical equipment and electronic products for functions like fixation, stretching, and resetting.
English hook tension springs are commonly used in products such as mobile phones, computers, gaming consoles, and other devices, including buttons, switches, connectors, car seat adjusters, door locks, engine hood support rods, mechanical devices, medical equipment, electronic and server equipment, as well as home appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and control panels or switches in these devices.
S-type retaining ring/E-type retaining ring
The retaining ring/clip, with shapes in the form of a C or E, uses elasticity to secure components onto shafts or within holes.
As a common mechanical part, retaining rings/clip play an important role in industrial design. By understanding the different types of retaining rings/clips and their characteristics, we can better select and apply them to ensure product reliability and durability.
How to choose the right tension spring?
Choosing a tension spring is a systematic process that requires consideration of multiple factors. Only by selecting the right tension spring can the equipment operate properly and have an extended service life.
Application environment: Understand the function of the spring in the equipment and its working conditions.
Calculate required tension: Determine the necessary spring force based on the load of the equipment.
Determine dimensions: Choose a spring that fits the installation space and meets the dimensional requirements of the customer's design.
Material selection: Select appropriate materials according to the working environment and desired lifespan.
Consult professionals: If there is uncertainty in spring selection, consult a professional spring manufacturer for advice.
Lifespan requirements: For applications requiring long life, choose high-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes.
Size constraints: Installation space limitations will affect the size of the spring.
Springs – Spiral Spring
Spiral Spring
A spiral spring is a type of spring made by winding strip-shaped material into a spiral form. Its defining feature is that one end is fixed while the other end twists, producing bending and elastic deformation under external force. Due to its unique structure and function, spiral springs are widely used across various fields.
High Energy Density: Capable of storing a large amount of energy within a limited space.
Torsional Elasticity: Stores and releases energy primarily through torsional deformation.
Variety in Size: Can be manufactured in various sizes and thicknesses to meet different application needs.
Strong Customizability: Can be designed with different force, torque, and lifespan according to specific customer requirements.
Spring - Surface Treatment Introduction
Springs – Introduction to Surface Treatments
As a common mechanical component, surface treatment plays a crucial role in extending the lifespan and improving the performance of springs. Different surface treatment methods provide various characteristics to meet a wide range of application requirements.
Why apply surface treatment to springs:
Rust and Corrosion Resistance: In humid or corrosive environments, surface treatments effectively prevent rust and extend the service life of the spring.
Enhanced Wear Resistance: Treatments can increase the surface hardness of the spring, reduce wear, and improve durability.
Improved Lubrication: Some surface treatments enhance the lubrication properties of the spring, reducing the friction coefficient.
Aesthetic Appeal: Treatments can enhance the visual appearance of springs, making them more attractive.
Common surface treatment methods for springs include:
Nickel plating, white zinc plating, blue zinc plating, yellow chromate zinc plating, black oxide coating, chrome plating, electrocoating, electrophoresis, baking paint, passivation, gold plating, tin plating, and more.
Factors to consider when choosing a surface treatment:
Spring Material: Different materials are suited for different surface treatments.
Working Environment: Temperature, humidity, and corrosiveness of the environment determine the suitable treatment.
Performance Requirements: Choose treatments based on corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or aesthetic needs.
Cost: Surface treatment costs vary, and need to be weighed against the performance benefits.
Spring surface treatment is a complex process that must be selected based on the specific application requirements. Proper surface treatment can significantly improve spring performance and service life, fulfilling the needs of various industrial applications.
What is an English Hook Extension Spring?
English Hook Extension Spring is a common type of extension spring characterized by its specially designed hooks at both ends. These hooks are typically bent at a 90-degree angle, allowing for easy attachment to other components. When tension is applied, the spring extends and stores energy, then returns to its original shape once the force is released.
Comparison Between Single Torsion Spring and Double Torsion Spring
Single Torsion Spring:
Composed of a single coiled wire that generates a torsional force when torque is applied.
Provides lower torque, has less stability, is simpler to manufacture, and is widely used in various applications.
Double Torsion Spring:
Made of two coiled wires wound in opposite directions. When torque is applied, the two coils work together to deliver greater torque.
Offers higher torque, greater stability, is more complex to manufacture, and is suitable for applications requiring higher torque or stability.
Why Choose a Double Torsion Spring?
Higher Torque Requirement: When the torque provided by a single torsion spring is insufficient, a double torsion spring can meet the demand.
Greater Stability: The dual-coil structure offers enhanced stability, is less prone to deformation, and provides a more reliable torque output.
More Complex Mechanical Properties: By adjusting the parameters of both coils, more complex mechanical characteristics can be achieved.
Both single and double torsion springs have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice depends on specific application requirements. Factors such as torque, stability, cost, and space should all be considered during selection.

Springs – An Introduction to Spring Fundamentals
A spring is a mechanical component that stores potential energy through elastic deformation. Simply put, it is a device that can be compressed or stretched and returns to its original shape once the external force is removed. Springs are widely used, appearing in everything from everyday items to precision instruments.
Springs come in various structures, with the most common type being the coil spring, which is the curled spring we often see in daily life. Based on the direction of the applied force, coil springs can be classified into:
1. Compression Spring:
2. Extension Spring:
3. Torsion Spring:
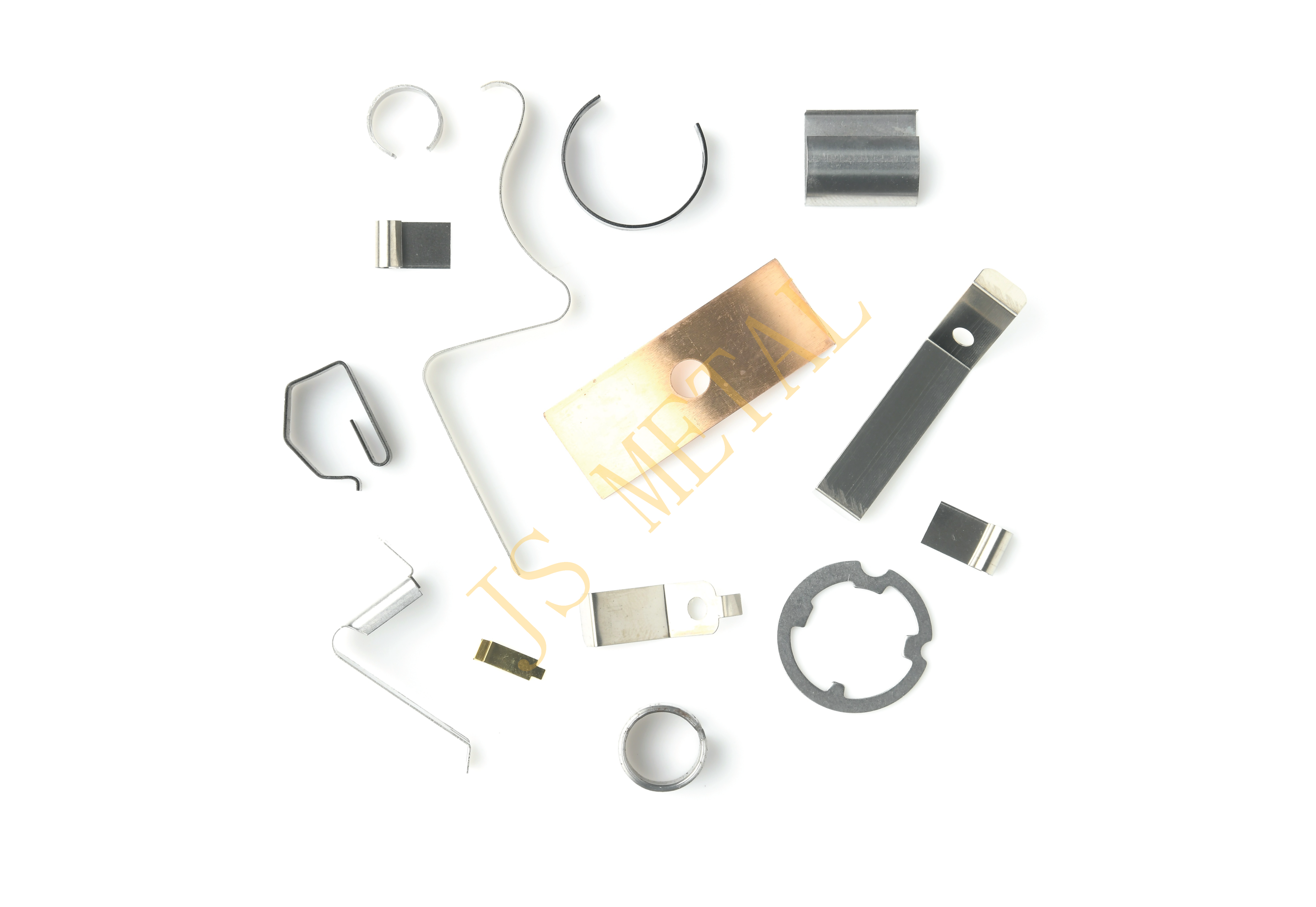
4. Wire Form (Bending Parts):
5. Retaining Clip / Snap Ring:
6. Spring Flat